Table of contents
- The TCP/IP Model: The Backbone of Digital Communication
- Revisiting the Packet Journey
- The Digital Compass: Protocols That Guide the Way
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol): The Reliable Courier
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol): The Speedy Messenger
- DNS (Domain Name System): The Digital Directory
- Everyday Guide: Configuring Your Home Wi-Fi
- What’s Next?
- Coming Up Next: Practical Networking Insights
- Conclusion
Welcome back, cyber enthusiasts! This week’s article is slightly longer than our previous ones. Each section not only introduces key concepts but also encourages proactive approaches to securing your home network. With many keywords making their first appearance, this piece serves as a simple yet instructive guide. Feel free to explore or skip sections based on your interests—there’s something here for everyone.
Last week, we unraveled the journey of data packets, bringing clarity to how networks connect us all. This week, we're taking it a step further by introducing the TCP/IP model—the practical framework that powers modern networks. We'll explore how data flows through its layers, highlight key protocols, and provide relatable, real-world applications. Think of it as a behind-the-scenes look at what keeps your digital world running smoothly.
The TCP/IP Model: The Backbone of Digital Communication
In the realm of networks, two models often emerge: the theoretical OSI Model and the practical TCP/IP Model. While the OSI model provides a comprehensive breakdown, the TCP/IP model governs your everyday internet usage.
It simplifies communication into four layers, each with a specific role:
Application Layer: Where user interaction happens, encompassing web browsers, email clients, and more.
Transport Layer: Ensures reliable data delivery by managing packet segmentation and reassembly.
Internet Layer: Handles routing and addressing, ensuring data finds its destination.
Network Interface Layer: Manages hardware and local connections, transmitting data physically.
By focusing on functionality, the TCP/IP model directly reflects how networks operate in real life, making it easier to understand and apply.
Revisiting the Packet Journey
In last week’s blog, Emma sent a photo to Liam. Let’s revisit their story through the lens of the TCP/IP model. When Emma hits “Send,” her photo embarks on a journey through these four layers:
Application Layer: Emma’s app converts the photo into data and initiates the transfer using a protocol like HTTPS.
Transport Layer: TCP breaks the photo into packets and ensures they are delivered in order.
Internet Layer: IP assigns Liam’s address to each packet and routes them efficiently.
Network Interface Layer: Wi-Fi hardware sends the packets over the physical medium to Liam’s device.

Source : thegeekstuff - TCP/IP Fundamentals
The Digital Compass: Protocols That Guide the Way
Protocols are the rules that govern how data moves through each TCP/IP layer. Let’s explore the most important ones in detail:
IP (Internet Protocol): The Addressing Guru
What It Does: IP ensures that every data packet knows exactly where to go. Each device connected to a network has a unique IP address, similar to a home address.
Types of IP Addresses:
IPv4: The widely used format (e.g., 192.168.1.1).
IPv6: A newer format designed to handle the growing number of devices (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3::8a2e:0370:7334).
Practical Tip: In your Wi-Fi router settings, consider assigning static IP addresses to devices like printers, smart TVs, or security cameras to avoid connection issues. Navigate to the DHCP Settings section in your router’s admin panel.
Key Takeaways:
Use IPv6 where possible to future-proof your network.
Assign static IPs to critical devices for better stability.
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol): The Reliable Courier
What It Does: TCP focuses on reliability, ensuring that all packets arrive in order and without loss.
How TCP Works:
Establishes a handshake (SYN, SYN-ACK, ACK) to confirm the connection. Think of this as two devices agreeing to connect by exchanging confirmation messages.
Breaks data into packets and numbers them for reassembly.
Retransmits lost packets.
Real-World Example: Watching a Netflix show? TCP ensures you get every frame of your video in the correct sequence.
Practical Tip: Enable Quality of Service (QoS) on your router to prioritize TCP traffic for important applications like video calls and streaming.
Key Takeaways:
TCP ensures reliability, making it ideal for streaming and downloads.
QoS settings can optimize your network for critical applications.
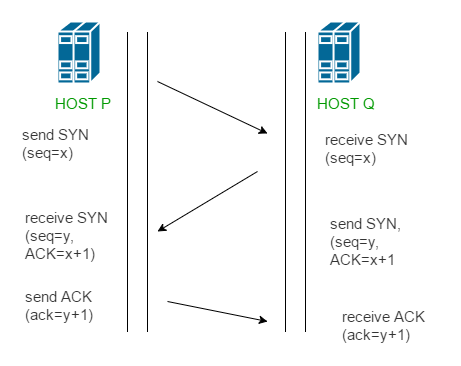
Source : GeeksforGeeks - TCP 3 way handshake process
UDP (User Datagram Protocol): The Speedy Messenger
What It Does: Unlike TCP, UDP prioritizes speed over reliability. It’s perfect for time-sensitive applications like live-streaming, gaming, or video conferencing.
How UDP Works:
Sends packets without establishing a connection.
No retransmission of lost packets, reducing delays.
Real-World Example: When gaming online, UDP ensures your actions are transmitted instantly, even if a few packets are dropped.
Practical Tip: Check your router settings for UDP optimization options under advanced configurations. This can help reduce lag during gaming or live-streaming.
Key Takeaways:
Use UDP for real-time applications where speed matters.
Optimize your router settings for gaming and live-streaming.
DNS (Domain Name System): The Digital Directory
What It Does: DNS translates human-readable domain names (like www.example.com) into machine-readable IP addresses.
How DNS Works:
Your device queries a DNS server to resolve a domain name.
The server responds with the corresponding IP address, allowing your device to connect to the desired website.
Real-World Example: Typing "www.google.com" into your browser initiates a DNS query to find Google’s IP address.
Practical Tip: Update your DNS settings in your router to use faster, more secure servers like Google’s 8.8.8.8 or Cloudflare’s 1.1.1.1 for improved browsing performance.
Additional Detail: Secure DNS servers encrypt your queries, ensuring that your ISP or hackers can't easily track the websites you visit. This added layer of security prevents third-party tracking and boosts privacy.
Key Takeaways:
Secure DNS servers protect your privacy and improve browsing speed.
Consider using Cloudflare’s or Google’s DNS for enhanced security.
Source : Anthony Bouchard (iDownloadBlog)
Everyday Guide: Configuring Your Home Wi-Fi
Let’s make these concepts actionable by focusing on real-world Wi-Fi configurations. Below is a detailed guide based on common router settings. This guide will help users on macOS, Windows, and Linux understand and optimize their home networks.
Step 1: Access Your Router Settings
Open a browser and enter your router’s IP address (commonly 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1).
Log in using your admin credentials (often found on a sticker on your router).

Source : Audioholics - How to login to wireless router
Step 2: Explore Router Tabs and Settings
Status:
Shows connected devices, uptime, and bandwidth usage.
Significance: Helps monitor network activity and identify unauthorized devices.
Wireless Settings:
Configure Wi-Fi names (SSID), passwords, and security protocols (e.g., WPA3).
Pro Tip: Use unique SSIDs and strong passwords to secure your network.
Internet Settings:
Includes options for DNS configuration, static IP setup, and ISP details.
Pro Tip: Switch to secure DNS servers for better performance and privacy.
DHCP Settings:
Manages IP address allocation to devices on the network.
Pro Tip: Assign static IPs to critical devices for stability.
Advanced Settings:
Includes QoS, port forwarding, and firewall options.
Pro Tip: Prioritize traffic for work or streaming devices under QoS.
Security:
Configure firewalls, MAC filtering, and VPN settings.
Pro Tip: Enable WPA3 encryption and MAC filtering to block unauthorized devices.
Logs:
Displays activity logs for troubleshooting and monitoring.
Pro Tip: Check logs for unusual traffic that may indicate security issues.
Step 3: Customize for Your Needs
For macOS Users: Navigate to System Preferences > Network to configure IP and DNS settings.
For Windows Users:
Go to Control Panel > Network and Sharing Center > Change Adapter Settings.
Right-click your network > Properties > IPv4 Settings to customize IP and DNS.
For Linux Users: Use the Network Manager GUI or terminal commands like nmcli to adjust settings.
Step 4: Regular Maintenance
Update Firmware: Check the router manufacturer’s website for the latest updates.
Restart Periodically: Clear temporary glitches by rebooting your router once a month.
Quick Tips for a Safer Home Network:
Use WPA3 encryption for enhanced Wi-Fi security.
Assign static IP addresses to critical devices like printers and smart TVs for better stability.
Switch to secure DNS servers (e.g., Google 8.8.8.8, Cloudflare 1.1.1.1) to improve browsing speed and privacy.
What’s Next?
Sometimes, a quick 5- to 6-minute read isn’t enough to dive into the depths of a topic. On that note, I’m excited to announce a new project I’ve been working on: a comprehensive networking guide designed with beginners in mind. My goal is to break down complex concepts and make networking fundamentals more accessible, so anyone can approach them with confidence. While it’s still a work in progress, I’ll be sharing valuable insights and practical tips along the way in further articles to come to help you build a solid foundation.
Coming Up Next: Practical Networking Insights
As we’ve laid the foundation with some key networking concepts, it’s time to dive deeper. In the upcoming technical articles, I’ll be exploring hands-on topics that will help you elevate your networking skills:
A Beginner’s Guide to VLANs: What They Are and How to Set Them Up
Learn what Virtual LANs (VLANs) are, why they matter, and how you can set them up to enhance network security and efficiency.Demystifying Subnetting: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
Subnetting doesn’t have to be complicated! In this article, I’ll break down subnetting step by step, showing you how to divide a network into smaller, manageable segments.Wi-Fi Security: How to Protect Your Wireless Network from Common Threats
Discover practical strategies for securing your Wi-Fi network and protecting it from common vulnerabilities, ensuring your data stays safe and sound.
Conclusion
Understanding network protocols and configurations is crucial in today's interconnected world. From the TCP/IP model’s layered approach to real-world applications like optimizing home Wi-Fi, these foundational concepts empower you to navigate the digital maze confidently. Whether you’re fine-tuning your router, securing your network, or exploring advanced protocols, the journey of learning never stops. Keep exploring, stay curious, and look forward to the deeper dives ahead!

